How to Change Font in HTML
In HTML, fonts play a crucial role in the overall design and readability of a web page. By using CSS, you can easily change the font style, size, color, and other properties to customize the appearance of text on your website. In this article, we will explore different ways to change the font in HTML using CSS.
1. Changing Font Family
You can change the font family in HTML by specifying different font names in your CSS. Here’s an example:
Output:

2. Changing Font Size
To change the font size in HTML, you can use the font-size property in CSS. Here’s an example:
Output:

3. Changing Font Color
You can change the font color in HTML by using the color property in CSS. Here’s an example:
Output:

4. Changing Font Weight
To change the font weight in HTML, you can use the font-weight property in CSS. Here’s an example:
Output:

5. Changing Font Style
You can change the font style in HTML by using the font-style property in CSS. Here’s an example:
Output:

6. Using Google Fonts
Google Fonts is a popular service that allows you to easily embed custom fonts into your website. Here’s an example of how to use Google Fonts:
Output:

7. Specifying Font Size in Different Units
You can specify the font size in HTML using different units such as pixels, em, rem, etc. Here’s an example:
Output:
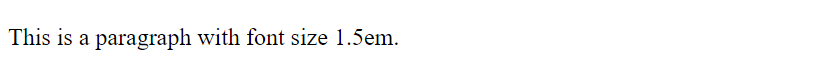
8. Using Web Safe Fonts
Web safe fonts are fonts that are commonly found on all operating systems and devices. Here’s an example of using web safe fonts:
Output:

9. Changing Font Decoration
You can change the font decoration in HTML using the text-decoration property in CSS. Here’s an example:
Output:

10. Changing Font Alignment
You can change the font alignment in HTML using the text-align property in CSS. Here’s an example:
Output:

Conclusion
In conclusion, changing the font in HTML is a simple and effective way to enhance the visual appeal of your website. By using CSS properties such as font-family, font-size, color, and others, you can customize the appearance of text to suit your design requirements. Experiment with different font styles and properties to create a unique and engaging user experience on your website.
 How HTML
How HTML